Stream API
Stream API is used to process collections of objects. A stream in Java is a sequence of objects that supports various methods which can be pipelined to produce the desired result.
- 1. Stream API is a way to express and process collections of objects.
- 2. Enable us to perform operations like filtering, mapping,reducing and sorting.
Syntax: Stream<T> stream;
Here T is either a class, object, or data type depending upon the declaration.
Features of Java8 Streams
- 1. A stream is not a data structure instead it takes input from the Collections, Arrays or I/O channels.
- 2. Streams don’t change the original data structure, they only provide the result as per the pipelined methods.
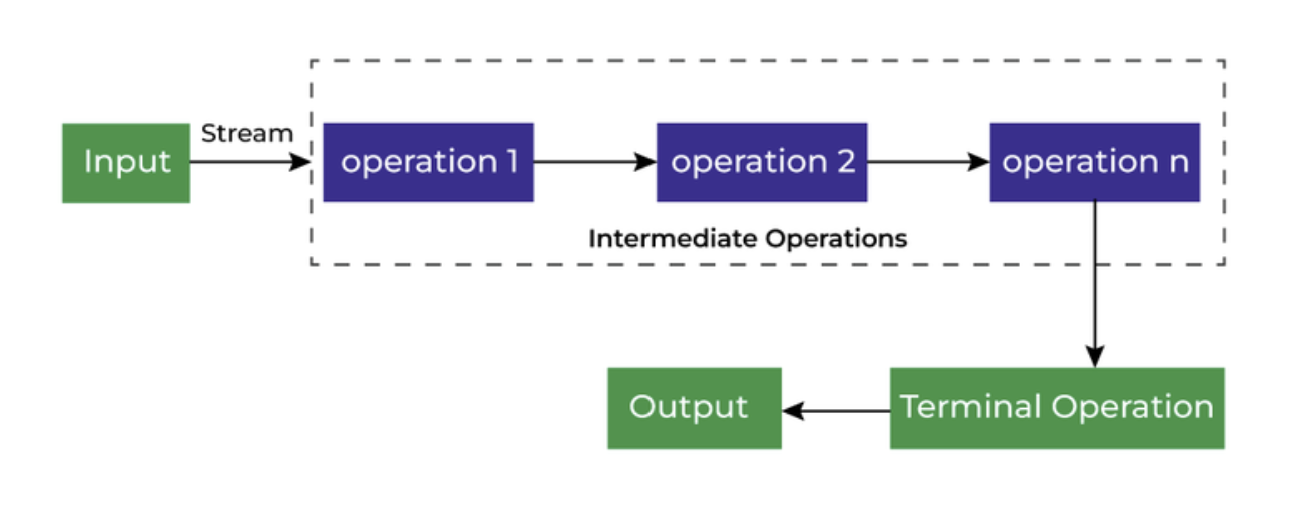
- 3. Each intermediate operation is lazily executed and returns a stream as a result, hence various intermediate operations can be pipelined. Terminal operations mark the end of the stream and return the result.
Different Operations On Streams
- 1. Intermediate Operations
- 2. Terminate Operations
1. Intermediate Operations
Intermediate Operations are the types of operations in which multiple methods are chained in a row.
Characteristics of Intermediate Operations
- 1. Methods are chained together.
- 2. Intermediate operations transform a stream into another stream.
- 3. It enables the concept of filtering where one method filters data and passes it to another method after processing.
Benefit of Java Stream
- - No Storage
- - Pipeline of Functions
- - Laziness
- - Can be infinite
- - Can be parallelized
- - Can be created from collections, arrays, Files Lines, Methods in Stream, IntStream etc.
Important Intermediate Operations
here are a few Intermediate Operations mentioned below:
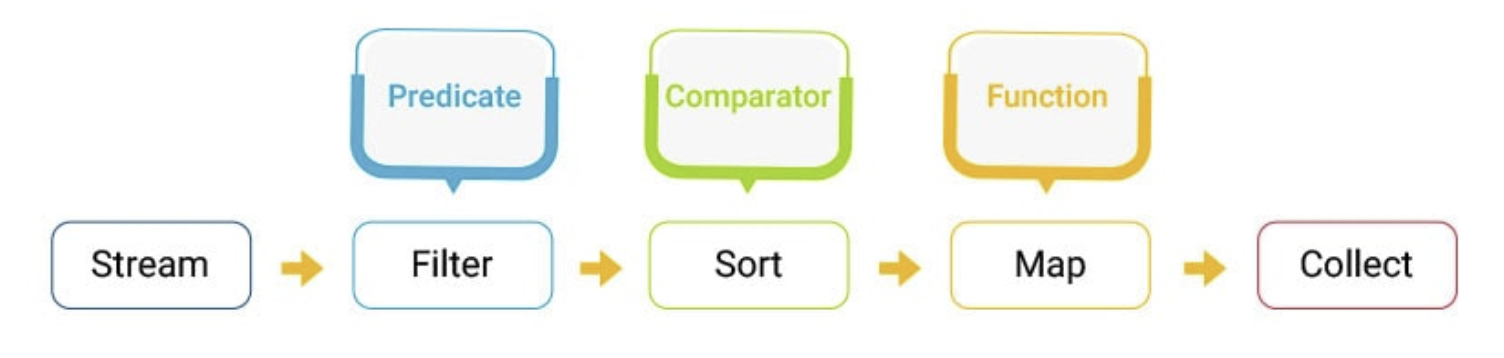
1. map():
The map method is used to return a stream consisting of the results of applying the given function to the elements of this stream.
List number = Arrays.asList(2,3,4,5);
List square = number.stream().map(x->x*x).collect(Collectors.toList());
2. filter(): The filter method is used to select elements as per the Predicate passed as an argument.
List names = Arrays.asList("Reflection","Collection","Stream");
List result = names.stream().filter(s->s.startsWith("S")).collect(Collectors.toList());
3. sorted(): The sorted method is used to sort the stream.
List names = Arrays.asList("Reflection","Collection","Stream");
List result = names.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
2. Terminal Operations
Terminal Operations are the type of Operations that return the result. These Operations are not processed further just return a final result value.
Important Terminal Operations
1. collect(): The collect method is used to return the result of the intermediate operations performed on the stream.
List number = Arrays.asList(2,3,4,5,3);
Set square = number.stream().map(x->x*x).collect(Collectors.toSet());
2. forEach(): The forEach method is used to iterate through every element of the stream.
List number = Arrays.asList(2,3,4,5);
number.stream().map(x->x*x).forEach(y->System.out.println(y));
3. reduce(): The reduce method is used to reduce the elements of a stream to a single value. The reduce method takes a BinaryOperator as a parameter.
List number = Arrays.asList(2,3,4,5);
int even = number.stream().filter(x->x%2==0).reduce(0,(ans,i)-> ans+i);
Example:
// Java program to demonstrate
// the use of stream in java
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
class Demo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create a list of integers
List<Integer> number = Arrays.asList(2, 3, 4, 5);
// demonstration of map method
List<Integer> square
= number.stream()
.map(x -> x * x)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// create a list of String
List<String> names = Arrays.asList(
"Reflection", "Collection", "Stream");
// demonstration of filter method
List<String> result
= names.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startsWith("S"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(result);
// demonstration of sorted method
List<String> show
= names.stream()
.sorted()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(show);
// create a list of integers
List<Integer> numbers
= Arrays.asList(2, 3, 4, 5, 2);
// collect method returns a set
Set<Integer> squareSet
= numbers.stream()
.map(x -> x * x)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(squareSet);
// demonstration of forEach method
number.stream()
.map(x -> x * x)
.forEach(y -> System.out.println(y));
// demonstration of reduce method
int even
= number.stream()
.filter(x -> x % 2 == 0)
.reduce(0, (ans, i) -> ans + i);
System.out.println(even);
}
}