Json Web Token
JSON Web Token, commonly referred to as JWT, is an open standard (RFC 7519) for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. The token is digitally signed, ensuring its authenticity and integrity. JWTs are primarily used to authenticate users, authorize access to certain resources, and exchange information securely.
JWT Structure
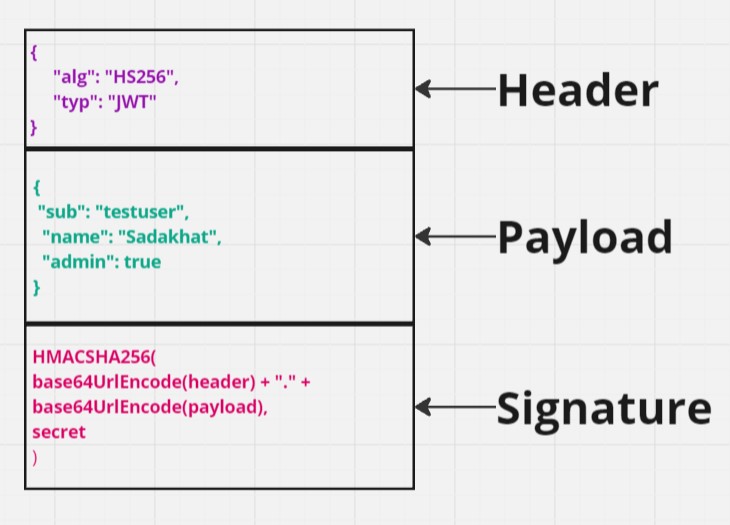
A JWT consists of three parts:
Header: The header typically consists of two parts — the token type (JWT) and the signing algorithm being used, such as HMAC SHA256 or RSA.
Payload: The payload contains the claims, which are statements about the user or other data. Claims can be of three types: registered, public, and private claims.
Signature: The signature can be created with encoded header, encoded payload, secret and the algorithm specified in header. The signature
is used to verify the sender of JWT is who and it will ensure that the message wasn't changed along the way.
JWT Working Principle
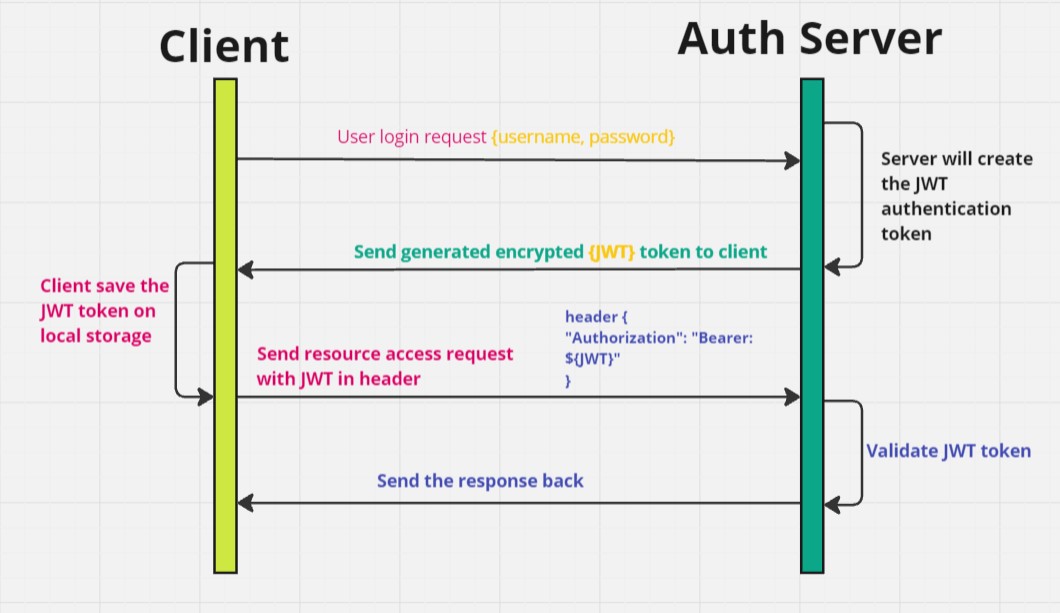
First client will send the login request to AuthServer along with username and password. Using these credentials server will create the JWT authentication token, this generated token will send back to the client. Client will store this token at his local storage and send the request by adding the JWT token in header to access the protected resources. Once server receives an request it will take the JWT token from the request header and validate the token, if token is valid then server will allow to access the protected resources and send the response accordingly back to the client.
Advantages of JWT
- Stateless: Since JWTs carry all the necessary information within themselves, the server doesn’t need to maintain session information. This makes JWTs stateless, which reduces server load and simplifies scalability.
- Compact and Efficient: Due to their compact size, JWTs are suitable for transmission over networks and are easily parsed by clients.
- Security: JWTs are digitally signed, ensuring data integrity and preventing tampering. Using encryption algorithms enhances the security further.
- Cross-Domain Communication: JWTs can be used across different domains or microservices since they don’t rely on cookies or server-side sessions.