SpringBoot Exception Handling
Spring Boot automatically take advantage of its default error-handling logic. Specifically, whenever an error occurs, a default response containing some information is returned. The problem is that this information may be poor or insufficient for the API callers to deal with the error properly.
Custom Exception handling in SpringBoot
Before SpringBoot 3.2, sprint where using @ExceptionHandler annotation to handle the exception.
Pros
- 1. @ExceptionHandler promotes cleaner code in many cases, it can also lead to increased complexity when dealing with a large number of exception types.
- 2. If not carefully managed, some exceptions might be overlooked or handled inappropriately. This can result in unexpected behavior or security vulnerabilities in your application.
- 3. Depending on the number of exception types and the complexity of your error responses, you may end up writing boilerplate code for handling exceptions and constructing error responses.
Cons
- 1. @ExceptionHandler allows you to define custom error-handling logic for specific exceptions or groups of exceptions.
- 2. You can control how exceptions are handled, log error information, and generate user-friendly error responses.
- 3. Separating error-handling logic into dedicated methods (annotated with @ExceptionHandler) keeps your controller methods cleaner and focused on their primary responsibilities.
This approach has a major drawback: The @ExceptionHandler annotated method is only active for that particular Controller, not globally for the entire application.
To overcome such drawbacks Since Spring 3.2 they introduced new solution called @ControllerAdvice annotation.
The @ControllerAdvice annotation allows us to consolidate our multiple, scattered @ExceptionHandlers into a single, global error-handling component.
- 1. It gives us full control over the body of the response as well as the status code.
- 2. It provides mapping of several exceptions to the same method, to be handled together.
- 3. It makes good use of the newer RESTful ResposeEntity response.
- 4. It provides global point of exception handle over the application rather than class level.
Besides that spring introduced @ResponseStatus annotation, which allows us to modify the HTTP status of our response. It can be applied in the following places:
- 1. On the exception class itself
- 2. Along with the @ExceptionHandler annotation on methods
- 3. Along with the @ControllerAdvice annotation on classes
Best Practices for Exception Handling in Spring Boot
Use informative error messages:
It is important to provide a clear and descriptive error message that explains the cause of the
exception. This will help developers quickly identify and resolve the issue.
Use HTTP status codes:
Spring Boot provides built-in support for mapping exceptions to HTTP status codes. Use these
status codes to provide a clear indication of the nature of the exception.
Use @ExceptionHandler:
Spring Boot provides the @ExceptionHandler annotation to handle exceptions thrown by a specific
controller method. This annotation can be used to
provide customized error responses for specific exceptions.
Use @ControllerAdvice:
The @ControllerAdvice annotation to handle exceptions globally across all controllers. This
annotation can be used to provide a centralized error
handling mechanism for an entire application.
Use loggers:
Use a logger to record details of the exception, including the stack trace, timestamp, and any
relevant context information.
Use custom exceptions:
Spring Boot allows you to define your own custom exceptions. Use these exceptions to provide
more specific error messages and to handle unique
exceptions that may not be covered by built-in Spring Boot exceptions.
Use error codes:
In addition to HTTP status codes, it can be useful to define your own error codes to provide
additional information about the cause of an
exception. These error codes can be included in the response body or in the logs, making it
easier to diagnose and fix issues. These error
codes may be domain specific error codes and then developer can easily understand.
Use validation:
Validating input data is an important part of preventing exceptions. Use validation annotations
to ensure that input data is valid before
processing it. This can help to prevent exceptions from occurring in the first place.
Let's see an example
I have written a simple SpringBoot application to show global exception handling. As part
of this I have created a package called "exception"
with class name as GlobalExceptionHandler. Also modified the service class to throw an
exceptions.
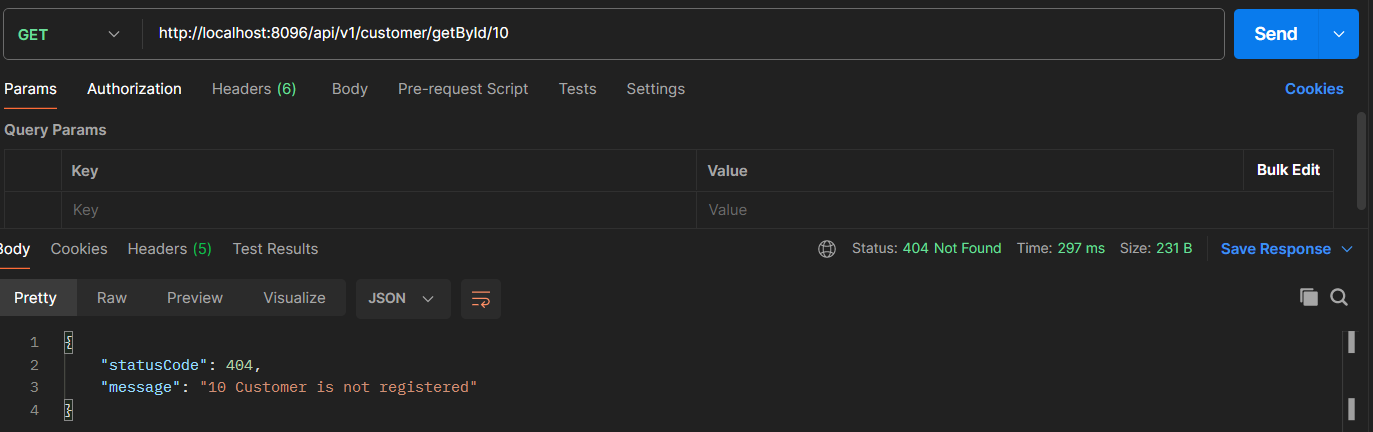
To validate exceptions throwing as expected, I have created the service with below endpoints.
- HTTP POST: /api/v1/customer/create
- HTTP GET: /api/v1/customer/getAll
- HTTP GET: /api/v1/customer/getById/{customerId}
Project Structure
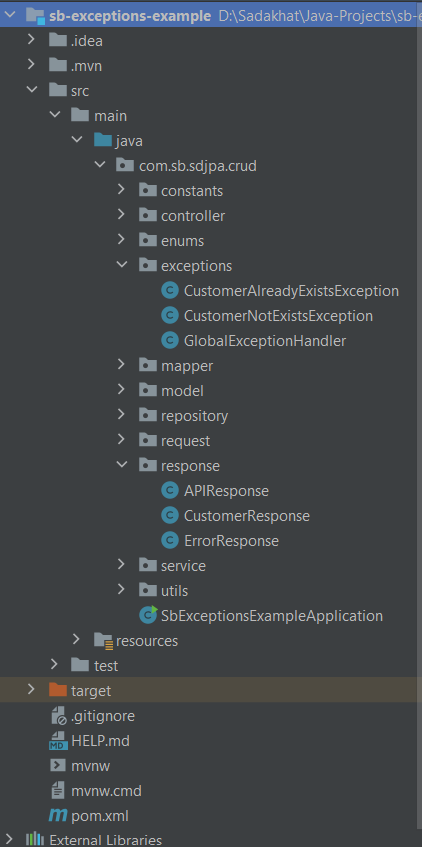
Exceptions
Created GlobalExceptionHandler class to handle the exception globally in the service, along with this I have created the two user defined exceptions those are CustomerNotExistsException and CustomerAlreadyExistsException
CustomerAlreadyExistsException.java
public class CustomerAlreadyExistsException extends RuntimeException {
public CustomerAlreadyExistsException() {}
public CustomerAlreadyExistsException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
CustomerNotExistsException.java
public class CustomerNotExistsException extends RuntimeException {
public CustomerNotExistsException() {}
public CustomerNotExistsException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
GlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.sb.sdjpa.crud.exceptions;
import com.sb.sdjpa.crud.response.ErrorResponse;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = CustomerNotExistsException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleCustomerNotExistsException(CustomerNotExistsException e) {
return ResponseEntity
.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
.body(ErrorResponse.builder()
.statusCode(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value())
.message(e.getMessage())
.build());
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = CustomerAlreadyExistsException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleCustomerExistsException(CustomerAlreadyExistsException e) {
return ResponseEntity
.status(HttpStatus.FOUND)
.body(ErrorResponse.builder()
.statusCode(HttpStatus.FOUND.value())
.message(e.getMessage())
.build()
);
}
}
CustomerServiceImpl
I have modified the service accordingly to handle the exceptions, check below program.
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
private final CustomerRepository customerRepository;
/**
* This method is used to store the customer details into the database.
*
* @param request customer request
* @return responseEntity object
*/
@Override
public ResponseEntity<APIResponse> createCustomer(CustomerRequest request) {
customerRepository
.findByCustomerMobileNumber(request.getCustomerMobileNumber())
.ifPresent(model -> {
throw new CustomerAlreadyExistsException(model.getCustomerMobileNumber() + " " + CUSTOMER_ALREADY_EXISTS);
});
CustomerModel customerModel = customerRepository.save(requestToModel(request));
return ResponseEntity.ok(
APIResponse.builder()
.errorCode(SUCCESS_CODE)
.errorMessage(SUCCESSFULLY_STORED)
.data(modelToResponseMapper(customerModel))
.build()
);
}
/**
* This method is used to fetch all the customers from the database.
*
* @return responseEntity object
*/
@Override
public ResponseEntity<APIResponse> getAllCustomers() {
List<CustomerModel> customerDetails = customerRepository.findAll();
List<CustomerResponse> customers = customerDetails.stream()
.map(customerModel -> modelToResponseMapper(customerModel))
.toList();
return ResponseEntity.ok(
APIResponse.builder()
.errorCode(SUCCESS_CODE)
.errorMessage(SUCCESSFULLY_RETRIEVED)
.data(customers)
.build()
);
}
/**
* Fetch customer based on the specific id.
*
* @param customerId customer id
* @return responseEntity object
*/
@Override
public ResponseEntity<APIResponse> getByCustomerId(long customerId) {
return customerRepository.findById(customerId)
.map(model -> ResponseEntity.ok(
APIResponse.builder()
.errorCode(SUCCESS_CODE)
.errorMessage(SUCCESSFULLY_RETRIEVED)
.data(modelToResponseMapper(model))
.build()
)).orElseThrow(() -> {
throw new CustomerNotExistsException(customerId + " " + CUSTOMER_NOT_EXISTS);
});
}
}
Full source code is available in follwong GitHub repository: SpringBoot Exceptions Example
Testing the exceptions through postman
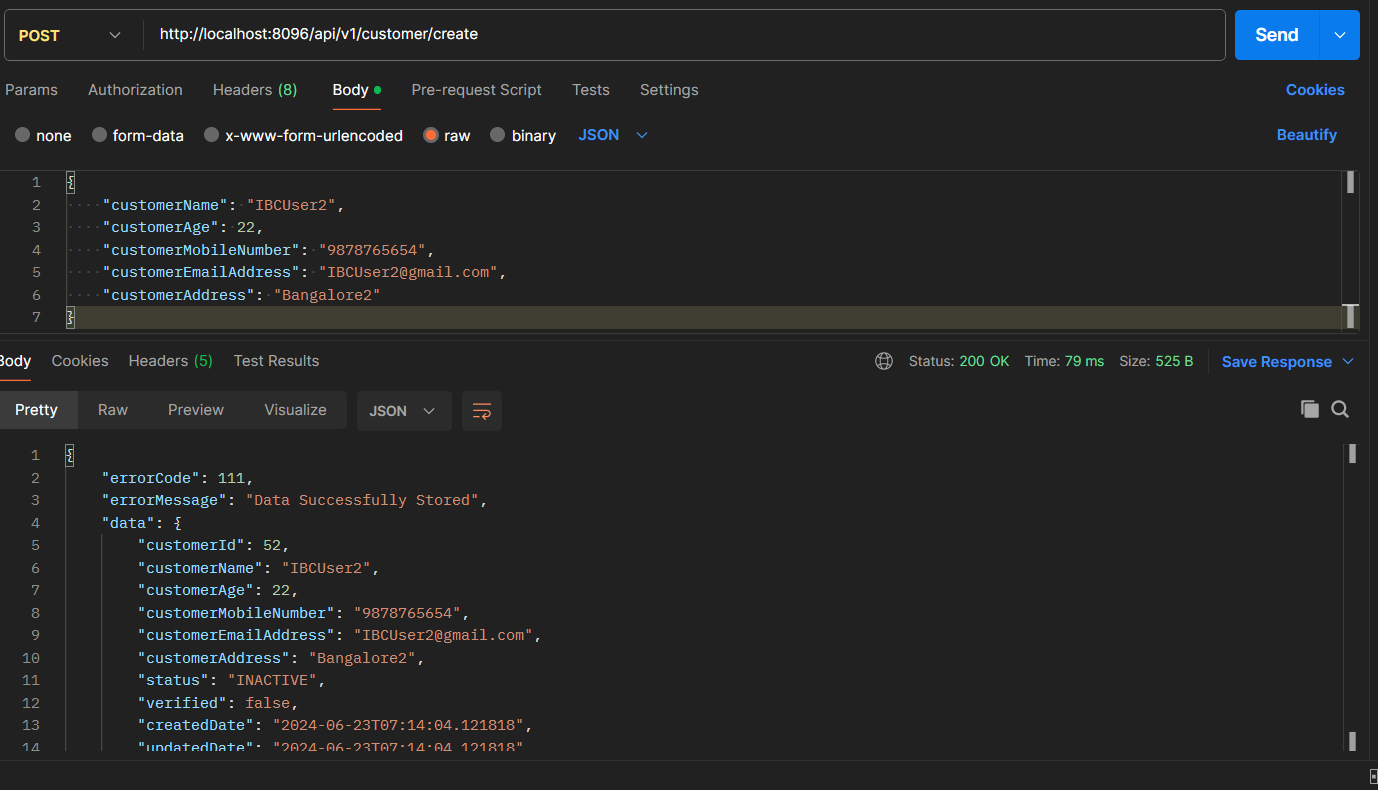
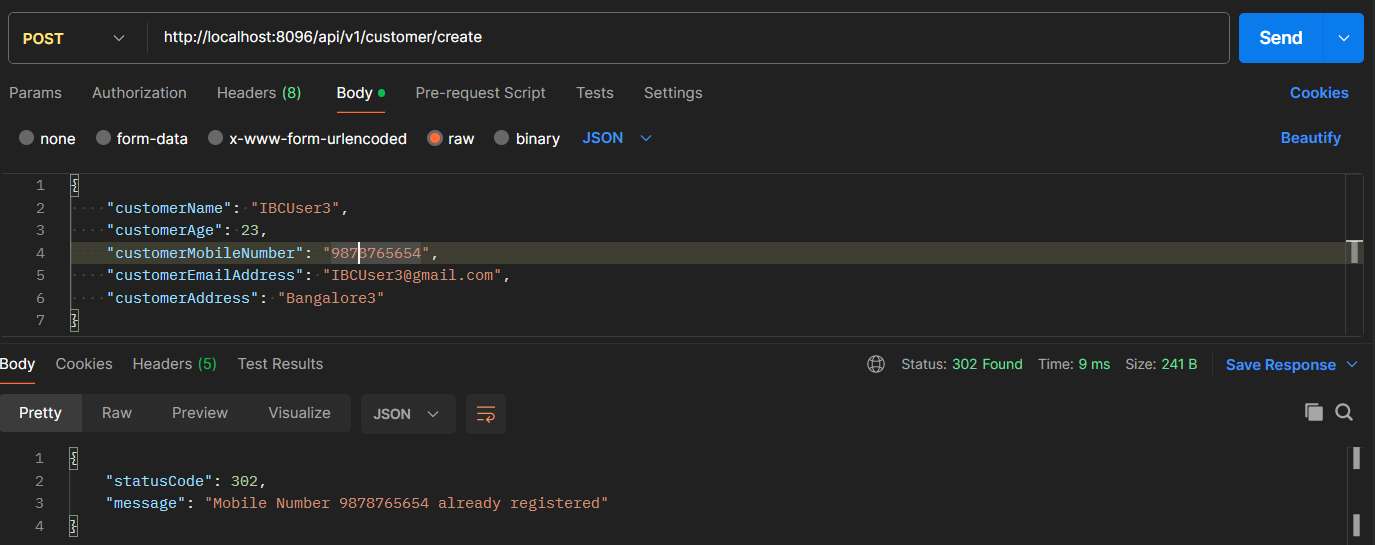
First, I will register a customer, post that using same mobile number will try to register the different customer, then will check for the exception.
Next one is Customer is not exists exception, let try to fetch the customer which is not available in the syste.