What is Spring Data JPA
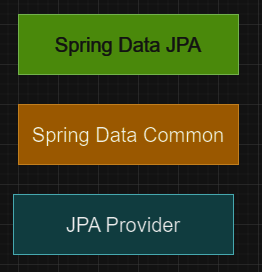
Spring Data JPA is not a JPA provider. It is a library / framework that adds an extra layer of abstraction on top of our JPA provider. If we decide to use Spring Data JPA, the repository layer of our application contains three layers that are described in the following:
- 1. Spring Data JPA provides support for creating JPA repositories by extending the Spring Data repository interfaces.
- 2. Spring Data Commons provides the infrastructure that is shared by the datastore specific Spring Data projects.
- 3. The JPA Provider implements the Java Persistence API.
Spring Data Repositories
The power of Spring Data JPA lies in the repository abstraction that is provided by the Spring Data Commons project and extended by the datastore specific sub-projects.
We can use Spring Data JPA without paying any attention to the actual implementation of the repository abstraction, but we have to be familiar with the Spring Data repository interfaces. These interfaces are described in the following.
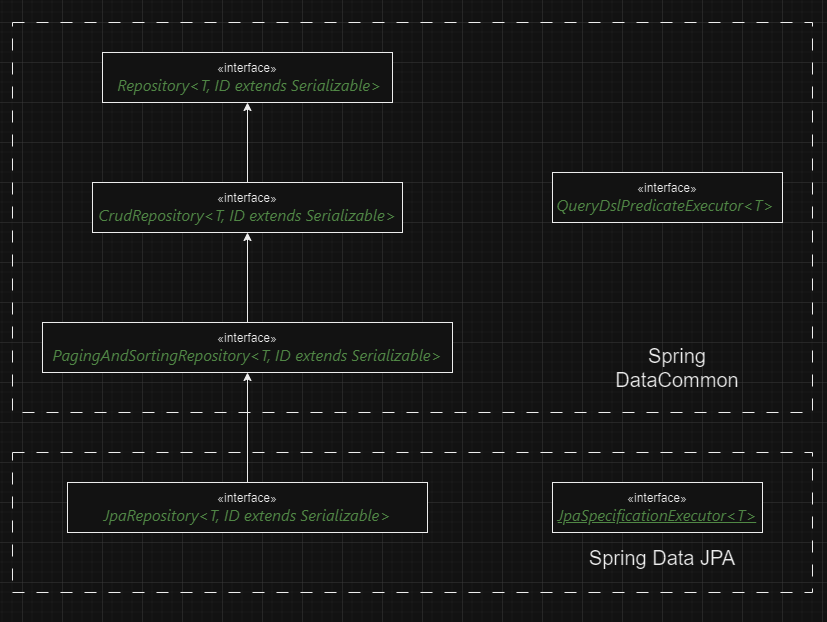
First, the Spring Data Commons project provides the following interfaces:
-
- The Repository<T, ID extends Serializable> interface is a marker interface that has two
purposes
- 1. It captures the type of the managed entity and the type of the entity’s id.
- 2. It helps the Spring container to discover the "concrete" repository interfaces during classpath scanning.
- - The CrudRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> interface provides CRUD operations for the managed entity.
- - The PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> interface declares the methods that are used to sort and paginate entities that are retrieved from the database.
- - The QueryDslPredicateExecutor<T> interface is not a "repository interface". It declares the methods that are used to retrieve entities from the database by using QueryDsl Predicate objects.
Second, the Spring Data JPA project provides the following interfaces:
- - The JpaRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> interface is a JPA specific repository interface that combines the methods declared by the common repository interfaces behind a single interface.
- - The JpaSpecificationExecutor<T> interface is not a "repository interface". It declares the methods that are used to retrieve entities from the database by using Specification<T> objects that use the JPA criteria API.