SpringBoot PostMapping Example
PostMapping example to register the customer. Here, will learn how to use @PostMapping annotation to handle the HTTP POST requests.
- HTTP POST /api/v1/customer/create – create a customer.
Will perform the simple customer registration operation without using without database storage.
Customer registration using following fields:
- customerName
- customerAge
- customerMobileNumber
- customerEmailAddress
- customerAddress
@PostMapping annotation is a simplified compact version of @RequestMapping(method-RequestMathod.POST)
SpringBoot provides a web tool to generate a initial bootstrap applicaiton which is Spring Initializer. If you want to learn the more about Spring initializer and how to use it to create the application visit following tutorial Create Springboot Application.
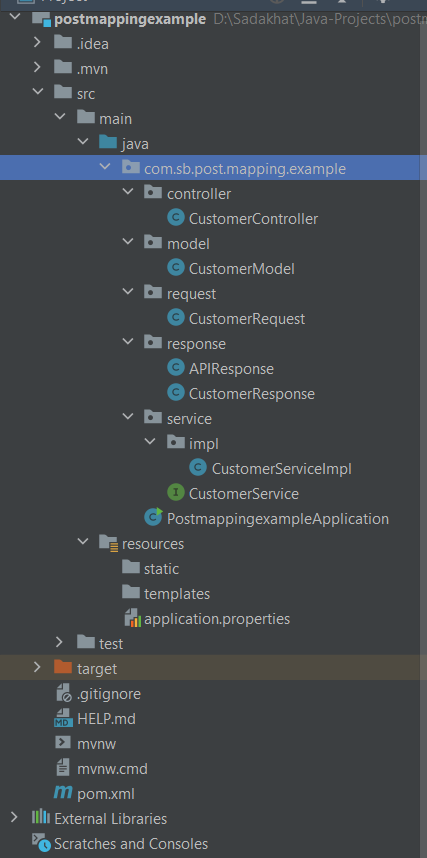
Project Strucure
pom.xml
While generating the SpringBoot project, will make sure that to add following Maven dependencies.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.sb.post.mapping.example</groupId>
<artifactId>postmappingexample</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>postmappingexample</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Request Payload
{
"customerName": "testUser1",
"customerAge": 20,
"customerMobileNumber": "77022898271",
"customerEmailAddress": "sadakhat11.khan@gmail.com",
"customerAddress": "Bangalore"
}
PostmappingexampleApplication.java
package com.sb.post.mapping.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class PostmappingexampleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PostmappingexampleApplication.class, args);
}
}
Request.java
package com.sb.post.mapping.example.request;
import lombok.*;
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
@Builder(toBuilder = true)
public class CustomerRequest {
private String customerName;
private int customerAge;
private String customerMobileNumber;
private String customerEmailAddress;
private String customerAddress;
}
@Getter: This annotation will help to enable the all getter methods.
@Setter: This annotation will help to enable the all setter methods.
@NoArgsConstructor: This annotation will help to enable the no argument NoArgsConstructor.
@AllArgsConstructor: This annotation will help to create the AllArgsConstructor.
@EqualsAndHashCode: This annotation will overrides the equals and hashcode method.
@Builder: This annotation will eliminates the need to write boilerplate code for constructors with
many
parameters. It generates the builder class and its methods automatically. this will allow us to set only the
fields that is needed, making it easy to work with classes that have many optional attributes.
CustomerController.java
package com.sb.post.mapping.example.controller;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.request.CustomerRequest;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.response.APIResponse;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.service.CustomerService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/customer")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CustomerController {
private final CustomerService customerService;
@PostMapping("/create")
public ResponseEntity<APIResponse> createCustomer(@RequestBody CustomerRequest request) {
return customerService.createCustomer(request);
}
}
@RestController: This annotation is used to indicate that this class is a REST controller, which
means it handles incoming HTTP requests
and returns the corresponsing responses.
@RequestMapping: This annotation is used to specifies the base URL path for all the request mappings
defined whith this controller.
@RequiredArgsConstructor: This annotation is used to generate the contructor with required arguments
to enable the construtor injection in
defined controller.
@PostMapping: This annotation is used to maps the specified method to the HTTP POST method for the
base URL path.
@RequestBody: This annotation is used to bind the request body to the CustomerRequest object,
which represents the CustomerRequest items to be added.
ResponseEntity: This object is used to send the HTTP response back to the client.
APIResponse.java
This we're going to use it as a common response object, will render all our responses and send back to the client.
package com.sb.post.mapping.example.response;
import lombok.*;
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
@Builder(toBuilder = true)
public class APIResponse {
private int errorCode;
private Object data;
}
CustomerService.java
package com.sb.post.mapping.example.service;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.request.CustomerRequest;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.response.APIResponse;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
public interface CustomerService {
ResponseEntity<APIResponse> createCustomer(CustomerRequest request);
}
CustomerModel.java
package com.sb.post.mapping.example.model;
import lombok.*;
import java.time.LocalDate;
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
@Builder(toBuilder = true)
public class CustomerModel {
private long customerId;
private String customerName;
private int customerAge;
private String customerMobileNumber;
private String customerEmailAddress;
private String customerAddress;
private LocalDate createdDate;
}
CustomerResponse.java
package com.sb.post.mapping.example.response;
import lombok.*;
import java.time.LocalDate;
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
@Builder(toBuilder = true)
public class CustomerResponse {
private long customerId;
private String customerName;
private int customerAge;
private String customerMobileNumber;
private String customerEmailAddress;
private String customerAddress;
private LocalDate createdDate;
}
CustomerServiceImpl.java
package com.sb.post.mapping.example.service.impl;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.model.CustomerModel;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.request.CustomerRequest;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.response.APIResponse;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.response.CustomerResponse;
import com.sb.post.mapping.example.service.CustomerService;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Service
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
private static List<CustomerModel> customers = new ArrayList<>();
private AtomicInteger c = new AtomicInteger(1);
@Override
public ResponseEntity<APIResponse> createCustomer(CustomerRequest request) {
CustomerModel customerModel = CustomerModel.builder()
.customerId(c.getAndIncrement())
.customerName(request.getCustomerName())
.customerAge(request.getCustomerAge())
.customerMobileNumber(request.getCustomerMobileNumber())
.customerEmailAddress(request.getCustomerEmailAddress())
.customerAddress(request.getCustomerAddress())
.createdDate(LocalDate.now())
.build();
customers.add(customerModel);
return ResponseEntity.ok(
APIResponse.builder()
.errorCode(000)
.data(CustomerResponse.builder()
.customerId(customerModel.getCustomerId())
.customerName(customerModel.getCustomerName())
.customerAge(customerModel.getCustomerAge())
.customerMobileNumber(customerModel.getCustomerMobileNumber())
.customerEmailAddress(customerModel.getCustomerEmailAddress())
.customerAddress(customerModel.getCustomerAddress())
.createdDate(customerModel.getCreatedDate())
.build()
)
.build()
);
}
}
application.properties
spring.application.name=postmappingexample
server.port=8080
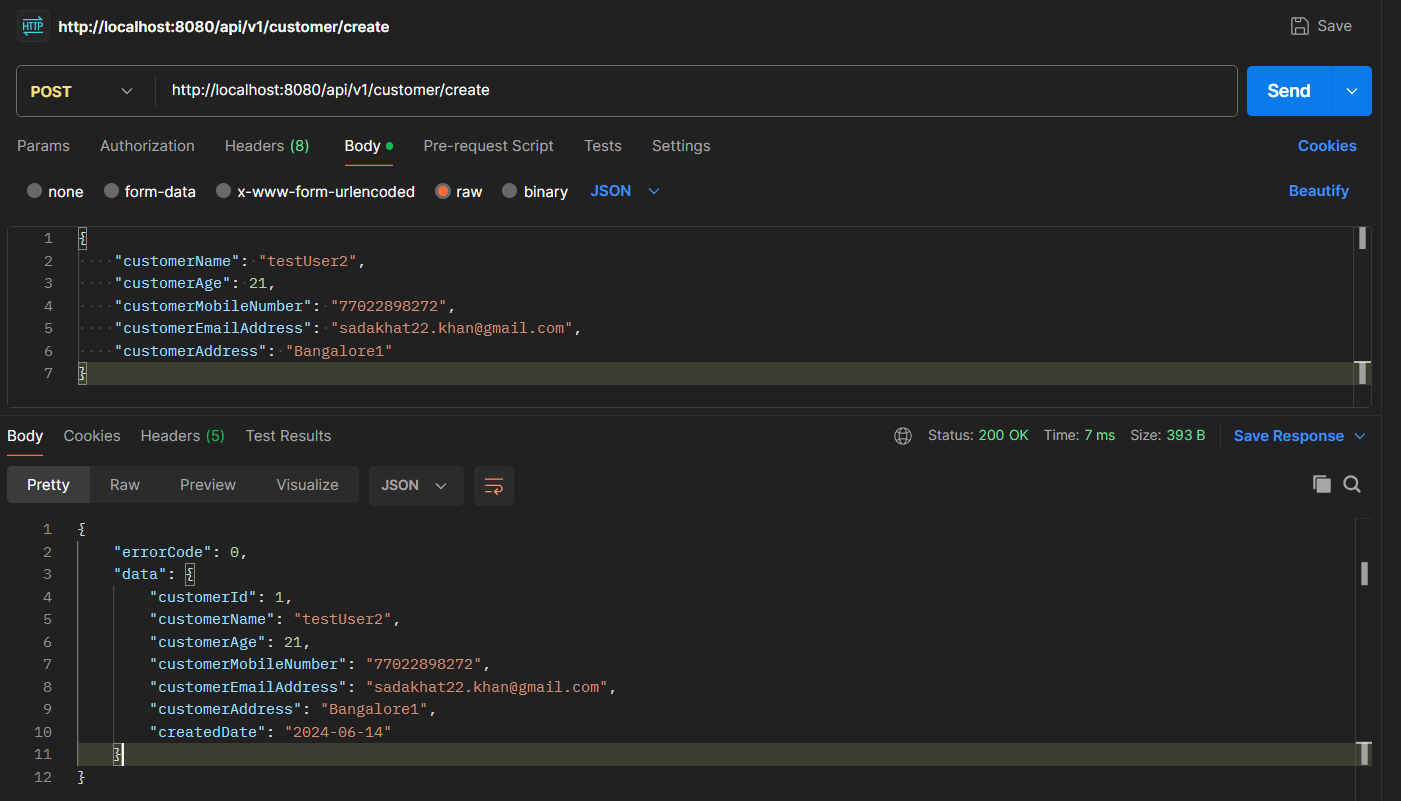
Postman
Register customer through postman API
Full source code is available in follwong GitHub repository: Postmapping example