Java Arrays
An array is a collection of same data types. For example storing 100 student names into a string array, 100 employee salaries into a float array type.
Declare an array
Array declaration, memory allocation can be like below, syntax is dataType[] and identifier. Here dataType can be any primitive type or objects and identifier is use to identify an array.
// declare an array
double[] doubleTypeArr;
// allocate memory
doubleTypeArr = new double[10];
// declare and allocate momory of an array in single line
double[] doubleTypeArr = new double[10];
Here, From above snippet the doubleTypeArr reference, is a used to store the double type of values into an array. If we want to allocate memory to an array then we need to allocate like above. It mean array can store 10 element. We can also tell that the size of an array is 10.
Initialize an Arrays
we can initialize arrays during declaration.
//declare and initialize and array
int[] studentAge = {12, 4, 5, 2, 5};
In above snippet we have created an array named studentAge and initialized it with different values. Here we have not provided the size of an array. In this case, the size will be automatically calculated by counting the no of elements in an array. In arrays, each memory location is associated with a number. The number is known as an array index. We can also initialize arrays in Java, using the index number.
// declare an array
int[] age = new int[5];
// initialize array
age[0] = 12;
age[1] = 4;
age[2] = 5;
age[3] = 2;
age[4] = 5;
Access Elements of an Array
We can access the element of an array using the index number. Here is the syntax for accessing elements of an array, array[index]
Access Array Elements
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an array
int[] age = {12, 4, 5, 2, 5};
// access each array elements
System.out.println("Accessing Elements of Array:");
System.out.println("First Element: " + age[0]);
System.out.println("Second Element: " + age[1]);
System.out.println("Third Element: " + age[2]);
System.out.println("Fourth Element: " + age[3]);
System.out.println("Fifth Element: " + age[4]);
}
}
Example: Using For Loop
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an array
int[] age = {12, 4, 5};
// loop through the array
// using for loop
System.out.println("Using for Loop:");
for(int i = 0; i < age.length; i++) {
System.out.println(age[i]);
}
}
}
Multidimensional Arrays
A multidimensional array is an array of arrays. In multidimensional array each element is an array itself. For example,
int[][] a = new int[3][4];
Here, we have created a multidimensional array named a. It is a 2-dimensional array, that can hold a maximum of 12 elements,
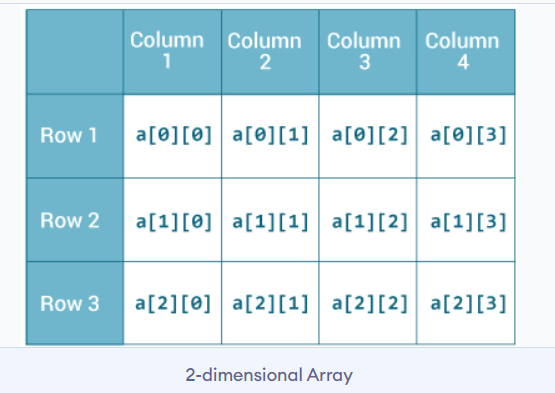
Remember, Java uses zero-based indexing, that is, indexing of arrays in Java starts with 0 and not 1. Let's take another example of the multidimensional array. 3-dimensional array example below,
String[][][] data = new String[3][4][2];
Here, data is a 3d array that can hold a maximum of 24 (3*4*2) elements of type String
Initialize a 2d array
Here is how we can initialize a 2-dimensional array in Java.
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};
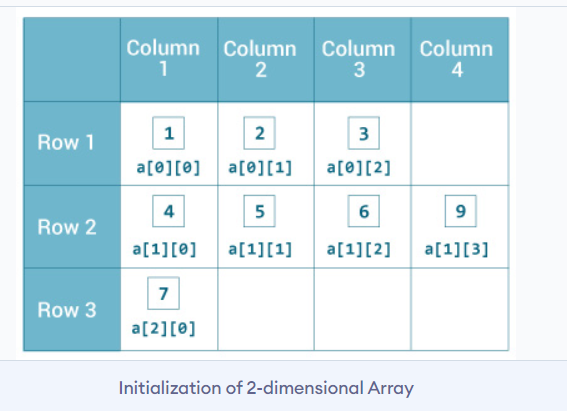
Print all elements of 2d array Using Loop
class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = {
{1, -2, 3},
{-4, -5, 6, 9},
{7},
};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < a[i].length; ++j) {
System.out.println(a[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
Initialize a 3d array
int[][][] test = {
{
{1, -2, 3},
{2, 3, 4}
},
{
{-4, -5, 6, 9},
{1},
{2, 3}
}
};
Example program:
class ThreeArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a 3d array
int[][][] test = {
{
{1, -2, 3},
{2, 3, 4}
},
{
{-4, -5, 6, 9},
{1},
{2, 3}
}
};
// for..each loop to iterate through elements of 3d array
for (int[][] array2D: test) {
for (int[] array1D: array2D) {
for(int item: array1D) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
}
}