Java Stack
In Java Stack is a class which is available in java.util package. stack is a linear data structure that is used to store the collection of objects. It is based on Last-In-First-Out (LIFO). The stack data structure has the two most important operations that are push and pop. The push operation inserts an element into the stack and pop operation removes an element from the top of the stack.
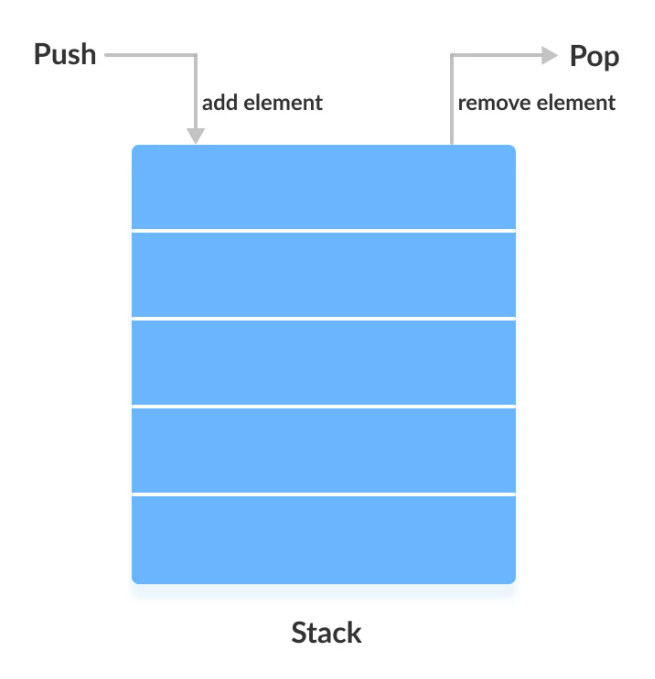
Creating a Stack
List list = new Stack();
(or)
Stack stack = new Stack();
Creating an Stack of a specific type
// create Integer type Stack
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
// create String type stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
In above we have created an Stack of two different types integer and string.
- ◈ If we create a Stack using Integer type then we can store only Integer type of element.
- ◈ If we create a Stack using String type then we can store only String type of element.
Methods of Stack class
Since Stack extends the Vector class, it inherits all the methods Vector. Stack class includes 5 more methods that distinguish it from Vector. There are some basic commonly used methods are:
| Method Name | Description |
|---|---|
| push() | To add an element to the top of the stack, we use the push() method. |
| pop() | To remove an element from the top of the stack, we use the pop() method. |
| peek() | The peek() method returns an object from the top of the stack. |
| search() | To search an element in the stack, we use the search() method. It returns the position of the element from the top of the stack. |
| empty() | To check whether a stack is empty or not, we use the empty() method. |
Basic Operations on Stack
The Stack class provides various methods to perform different operations on Stack. We will look at some commonly used Stack operations.
- ▪ Push elements
- ▪ Pop elements
- ▪ Peek elements
- ▪ Search elements
- ▪ Empty elements
Push, Example program:
import java.util.Stack;
public class PushExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<String>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
}
}
Pop, Example program:
import java.util.Stack;
public class PopExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<String>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + animals);
// Remove element stacks
String element = animals.pop();
System.out.println("Removed Element: " + element);
}
}
Peek, Example program:
import java.util.Stack;
public class PeekExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<String>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
// Access element from the top
String element = animals.peek();
System.out.println("Element at top: " + element);
}
}
Search, Example program:
import java.util.Stack;
public class SearchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<String>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
// Search an element
int position = animals.search("Horse");
System.out.println("Position of Horse: " + position);
}
}
Empty, Example program:
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<String>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
// Check if stack is empty
boolean result = animals.empty();
System.out.println("Is the stack empty? " + result);
}
}