Java Map Interface
Map is an interface which is available in java.util package. The Map interface of the Java collections framework provides the functionality of the map data structure. In Java Map, elements are stored in key/value pairs. Keys are unique values associated with individual values. Map cannot contains duplicate keys.

In the above diagram, we have values: United States, Brazil, and Spain. And we have corresponding keys: us, br, and es. Now, we can access those values using their corresponding keys.
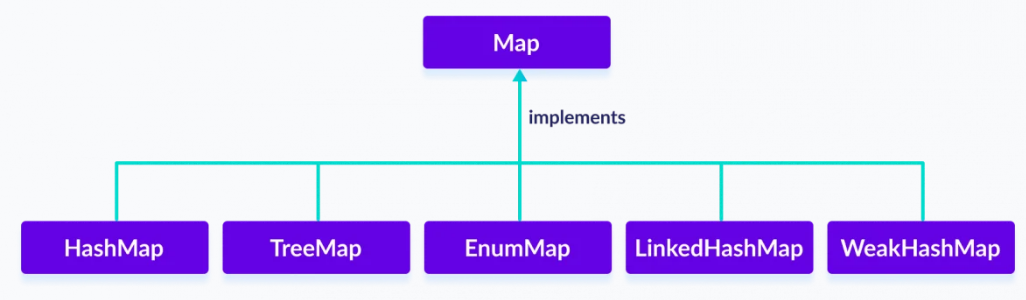
Map interface has 5 different types of class, In order to use functionalities of the Map interface, we can use these classes:
- 1. HashMap
- 2. TreeMap
- 3. EnumMap
- 4. LinkedHashMap
- 5. WeakHashMap
Map interface extended by three different subinterfaces:
- 1. SortedMap
- 2. NavigableMap
- 3. ConcurrentMap

The Map interface includes all the methods of the Collection interface. It is because Collection is a super interface of Map. Besides methods available in the Collection interface, the Map interface also includes the following methods:
- ◈ put(K, V) - Inserts the association of a key K and a value V into the map. If the key is already present, the new value replaces the old value.
- ◈ putAll() - Inserts all the entries from the specified map to this map.
- ◈ putIfAbsent(K, V) - Inserts the association if the key K is not already associated with the value V.
- ◈ get(K) - Returns the value associated with the specified key K. If the key is not found, it returns null.
- ◈ getOrDefault(K, defaultValue) - Returns the value associated with the specified key K. If the key is not found, it returns the defaultValue.
- ◈ containsKey(K) - Checks if the specified key K is present in the map or not.
- ◈ containsValue(V) - Checks if the specified value V is present in the map or not.
- ◈ replace(K, V) - Replace the value of the key K with the new specified value V.
- ◈ replace(K, oldValue, newValue) - Replaces the value of the key K with the new value newValue only if the key K is associated with the value oldValue.
- ◈ remove(K) - Removes the entry from the map represented by the key K.
- ◈ remove(K, V) - Removes the entry from the map that has key K associated with value V.
- ◈ keySet() - Returns a set of all the keys present in a map.
- ◈ values() - Returns a set of all the values present in a map.
- ◈ entrySet() - Returns a set of all the key/value mapping present in a map.