Java Deque Interface
The Deque interface of the Java collections framework provides the functionality of a double-ended queue. It extends the Queue interface.
There are 2 different classes in Deque interface.
- ▪ ArrayDeque
- ▪ LinkedList
Working of Deque
In a regular queue, elements are added from the rear and removed from the front. However, in a deque, we can insert and remove elements from both front and rear.
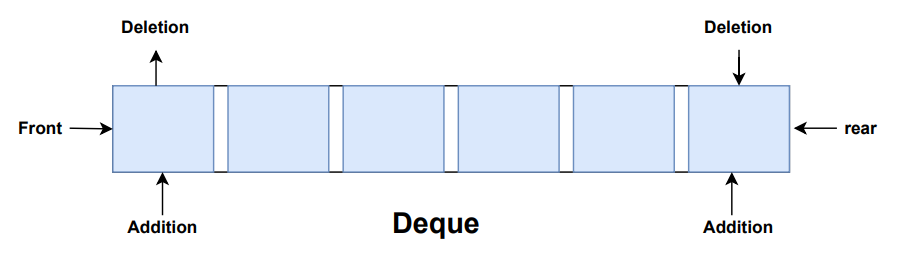
How to use Deque
we must import the java.util.Deque package to use Deque.
// Array implementation of Deque
Deque<String> animal1 = new ArrayDeque<>();
// LinkedList implementation of Deque
Deque<String> animal2 = new LinkedList<>();
Some of the commonly used methods of the Deque interface are:
- ◈ addFirst() - Adds the specified element at the beginning of the deque. Throws an exception if the deque is full.
- ◈ addLast() - Adds the specified element at the end of the deque. Throws an exception if the deque is full.
- ◈ offerFirst() - Adds the specified element at the beginning of the deque. Returns false if the deque is full.
- ◈ offerLast() - Adds the specified element at the end of the deque. Returns false if the deque is full.
- ◈ getFirst() - Returns the first element of the deque. Throws an exception if the deque is empty.
- ◈ getLast() - Returns the last element of the deque. Throws an exception if the deque is empty.
- ◈ peekFirst() - Returns the first element of the deque. Returns null if the deque is empty.
- ◈ peekLast() - Returns the last element of the deque. Returns null if the deque is empty.
- ◈ removeFirst() - Returns and removes the first element of the deque. Throws an exception if the deque is empty.
- ◈ removeLast() - Returns and removes the last element of the deque. Throws an exception if the deque is empty.
- ◈ pollFirst() - Returns and removes the first element of the deque. Returns null if the deque is empty.
- ◈ pollLast() - Returns and removes the last element of the deque. Returns null if the deque is empty.