Java Inheritance
Inheritance is nothing but Inheriting the properties from one class to another is called Inheritance. Or Extending the features from base-class to derived-class is called Inheritance. Or Inheritance is the technique which allows us inherit the data-members and methods from base-class to derived-class.
Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship.Advantages:
- a. Application development times is very less.
- b. Redundancy (repetition) of the code is reduced, so that it will take less memory, so we can get consistent results.
- c. Can achive runtime polymorphism (Method overriding)
- d. For code reusability
Types of Inheritances
In Java, we have five types of inheritance.
- a. Single Inheritance
- b. Multi-Level Inheritance
- c. Hierarchial Inheritance
- d. Multiple Inheritance
- e. Hybrid Inheritance
Single Inheritance
When a class inherits another class, it is known as a single inheritance. In the example given below, Dog class inherits the Animal class, so there is the single inheritance.
Example:
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class TestSingleInheritance {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Dog d = new Dog();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
Multi-Level Inheritance
When there is a chain of inheritance, it is known as multilevel inheritance. As you can see in the example given below, BabyDog class inherits the Dog class which again inherits the Animal class, so there is a multilevel inheritance.
Example:
class Animal{
void eat() {
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class BabyDog extends Dog {
void weep() {
System.out.println("weeping...");
}
}
class TestInheritance2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
BabyDog d = new BabyDog();
d.weep();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
Hierarchial Inheritance
When two or more classes inherits a single class, it is known as hierarchical inheritance. In the example given below, Dog and Cat classes inherits the Animal class, so there is hierarchical inheritance.
Example
class Animal{
void eat() {
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void bark() {
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
void meow() {
System.out.println("meowing...");
}
}
class TestInheritance3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Cat c = new Cat();
c.meow();
c.eat();
}
}
Multiple Inheritance
One class inherit multiple class called multiple inheritance. Example Class C inherits Class A and ClassB. Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance.
multiple inheritance is not supported in java
To reduce the complexity and simplify the language, multiple inheritance is not supported in java. Consider a scenario where A, B, and C are three classes. The C class inherits A and B classes. If A and B classes have the same method and you call it from child class object, there will be ambiguity to call the method of A or B class. Since compile-time errors are better than runtime errors, Java renders compile-time error if you inherit 2 classes. So whether you have same method or different, there will be compile time error.
Example:
class A{
void msg() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
class B{
void msg() {
System.out.println("Welcome");
}
}
class C extends A,B {//suppose if it were
public static void main(String args[]) {
C obj = new C();
obj.msg();//Now which msg() method would be invoked?
}
}
Hybrid Inheritance
A hybrid inheritance is a combination of more than one types of inheritance. For example when class A and B extends class C & another class D extends class A then this is a hybrid inheritance, because it is a combination of single and hierarchical inheritance.
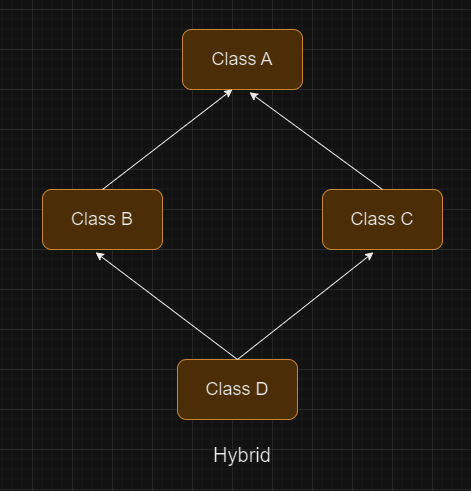
Example:
class C {
public void disp() {
System.out.println("C");
}
}
class A extends C {
public void disp() {
System.out.println("A");
}
}
class B extends C {
public void disp() {
System.out.println("B");
}
}
class D extends A {
public void disp() {
System.out.println("D");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
D obj = new D();
obj.disp();
}
}
Aggregation Has-A relation in Java
If a class have an entity reference, it is known as Aggregation. Aggregation represents HAS-A relationship. Consider a situation, Employee object contains many informations such as id, name, emailId etc. It contains one more object named address, which contains its own informations such as city, state, country, zipcode etc. as given below. In such case, Employee has an entity reference address, so relationship is Employee HAS-A address.
class Student {
int id;
String name;
Address address;//Address is a class
}
class Address {
String city;
String state;
String country:
}
When use Aggregation?
- 1. Code reuse is also best achieved by aggregation when there is no is-a relationship.
- 2. Inheritance should be used only if the relationship is-a is maintained throughout the lifetime of the objects involved; otherwise, aggregation is the best choice.