Java Queue Interface
The Queue is an interface, it is present in java.util package and it extends the Collection interface. Queue will process the elements in FIFO(First In First Out) order.
Queue interface classes.
- ▪ ArrayDeque
- ▪ LinkedList
- ▪ PriorityQueue
- ▪ Deque
- ▪ BlockingQueue
- ▪ BlockingDeque
Working of Queue data structures
In queues, elements are stored and accessed in First In, First Out manner. That is, elements are added from the behind and removed from the front.
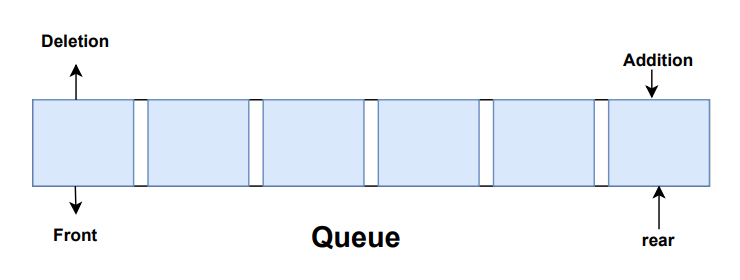
How to use Queue
We must import java.util.Queue package in order to use Queue
// LinkedList implementation of Queue
Queue<String< animal1 = new LinkedList<>();
// Array implementation of Queue
Queue<String< animal2 = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Priority Queue implementation of Queue
Queue<String< animal 3 = new PriorityQueue<>();
Some of the commonly used methods of the Queue interface are:
- ◈ add() - Inserts the specified element into the queue. If the task is successful, add() returns true, if not it throws an exception.
- ◈ offer() - Inserts the specified element into the queue. If the task is successful, offer() returns true, if not it returns false.
- ◈ element() - Returns the head of the queue. Throws an exception if the queue is empty.
- ◈ peek() - Returns the head of the queue. Returns null if the queue is empty.
- ◈ remove() - Returns and removes the head of the queue. Throws an exception if the queue is empty.
- ◈ poll() - Returns and removes the head of the queue. Returns null if the queue is empty.