SpringBoot-Kafka Tutorial
Apache Kafka Consumer: SpringBoot Microservice
Kafka Consumer - Introduction
In the following lessons, you will learn how to create a Spring Boot application that acts as Kafka consumer. If you see the below diagram, left side the product microservice that acts as a producer. Once the producer microservice publish a message to kafka topic, the consumer microservice will consumer that message from the topic.
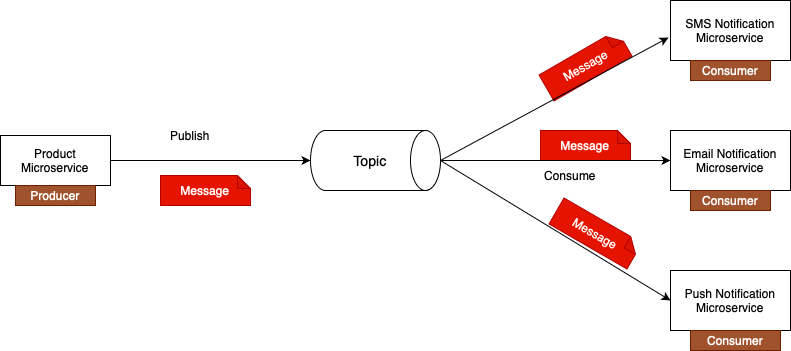
As shown in the above diagram the right side we have email notification microservice that act as kafka consumer, and it will be consuming new messages from Kafka topic. Once Kafka consumes message from a topic, it does not delete it. The message remains in the topic. So if needed, you can have more Kafka consumers running, and each of these Kafka consumers will receive their own copy of a message.
Let's have a look at a below diagram where we have a kafka topic. When producer puhlish the messages each message will store in its own partition. When we start the consumer microservice, it starts pulling messages from kafka topic at a regular time internal, which can be configured through configuration properties. When Kafka consumer reads messages from partitions, it reads them in parallel.
There is no order guarantee which messages from which partitions will be read first. But it does read messages in order within a single partition. There is no order guarantee between partitions.
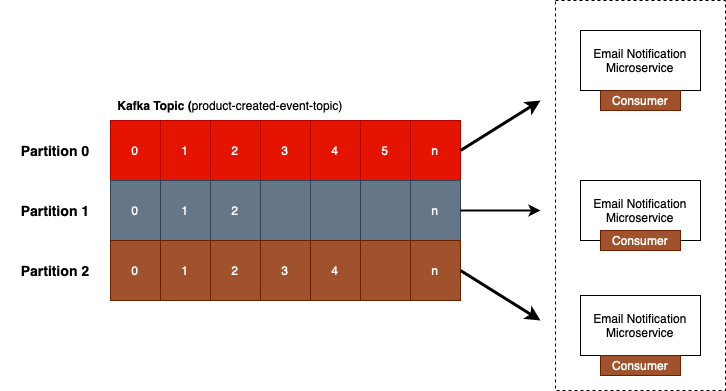
If you have a single application, then it will read messages from all three partitions. But if you have three consumers running, then each consumer will be assigned to read messages from one partition only. If you need to scale up your application and you want to start more instances of the same consumer microservice.
As shown in above diagram we can have three consumers which can read messages from the same topic. Each consumer reading messages from its own partition. This will help you process messages from Kafka topic faster.
Create EmailNotificationMicroservice using SpringBoot
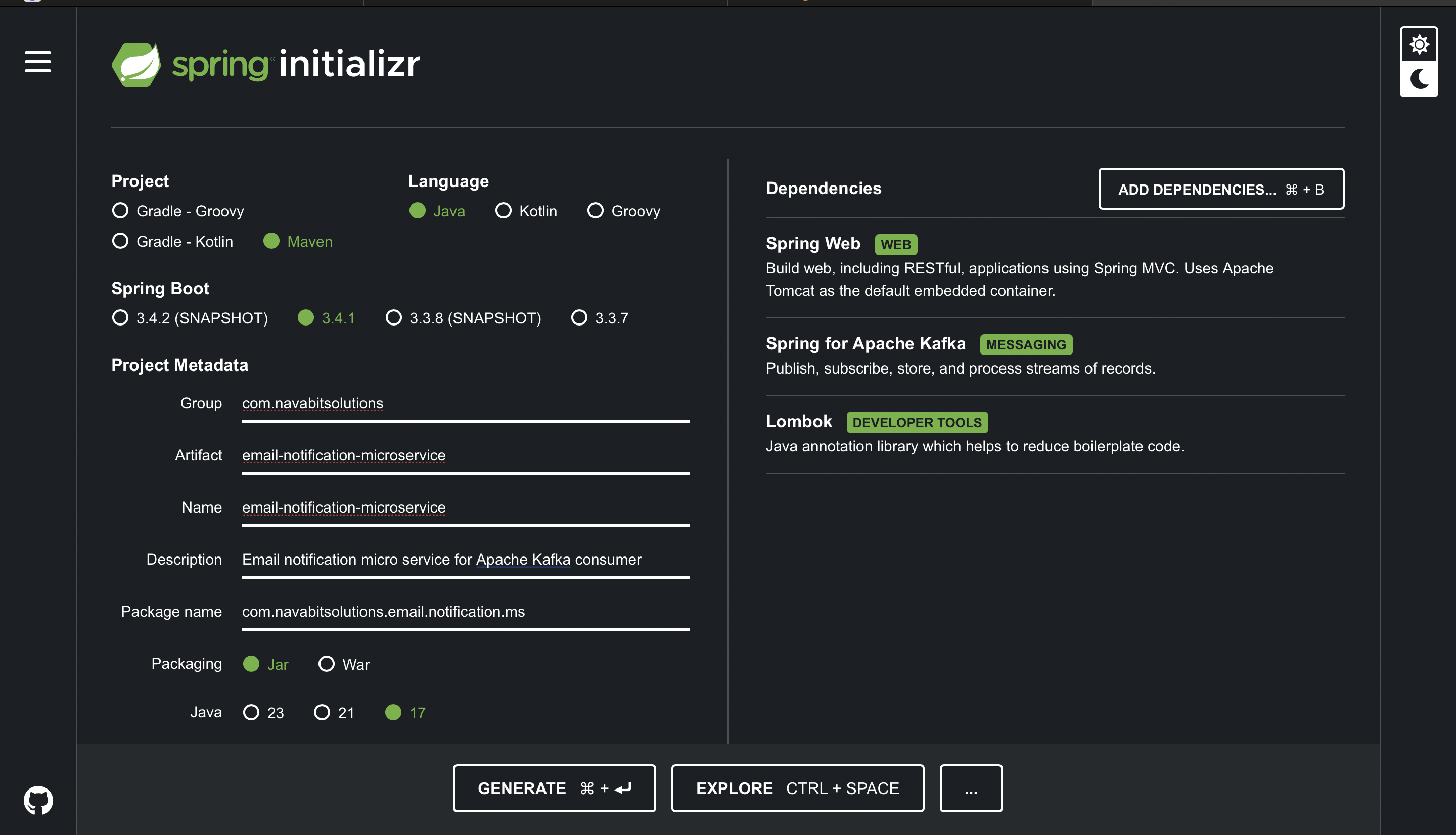
To create a new SpringBoot microservice project first you need to navigate to the start.spring.io. Next select project a as Maven, language as Java and then next select the SpringBoot version (I am selecting 3.4.1). Next we need to fill the Project Metadata then next packing as Jar and Java version as 17.
Next add the following dependencies and click on Generate button.
- 1. Spring Web
- 2. Spring for Apache Kafka
- 3. Lombok
Once project has been downloaded import the same project into your IntelliJ IDEA. And it looks like below in IDE
Kafka Consumer Configuration Properties
- server.port=0: It will make my email notification microservice start up on a random port number.
- spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers=localhost:9092,localhost:9094: This configuration property, it is used to specify a list of bootstrap servers and bootstrap server is used for initial connection to Kafka cluster.
- spring.kafka.consumer.key-deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeSerializer: It is used to specify the Deserializer class for Kafka message keys.
- spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer=org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonDeserializer: It is used to specify the Deserializer class that will be used to deserialize message value.
- spring.kafka.consumer.group-id=product-created-events: This is a group of microservices or a group of Kafka consumers that work together to consume messages from a topic and this property, it allows us to define a unique string that identifies consumer group.
- spring.kafka.consumer.properties.spring.json.trusted.packages=*: This configuration property, we specify one or more packages that are considered trusted for deserialization when processing Json messages.
Full code base is available in GitHub repository Kafka Consumer: Email Notification Microservice
Kafka Consumer with @kafkaEventListener and @kafkaHandler
Core Module
Next we need to create a centeralized core project which can be shared by both producer and consumner. To create a core project as we all know first we need to visit the start.spring.io. Next select project a as Maven, language as Java and then next select the SpringBoot version (I am selecting 3.4.1). Next we need to fill the Project Metadata then next packing as Jar and Java version as 17. Do not select any project dependencies, because this project will use it as a library.
Once we downloaded the project from start.sprint.io, next we need to modify the pom.xml. From pom.xml file and remove the spring-boot-starter and spring-boot-starter-test dependencies, and also remove the build tag. Once it is done create the ProductCreatedEvent object in core project.
Once project has been downloaded import the same project into your IntelliJ IDEA. Create an ProductCreatedEvent object in core module because its common between product (producer) and email-notification (consumer) microservices.
Once we created ProductCreatedEvent in core module, then next build the project and add it as maven dependency in both email-notification and product microservice. Next delete the ProductCreatedEvent.java file which is available in each service. Created core module to place all common object to share between both the microservices. Add below dependency in both microservices.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.kafka.ws.core</groupId>
<artifactId>core</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
Full code base is available in GitHub repository Kafka Consumer: core module for Microservices
Core project as project dependency
The above code dependency add in pom.xml of both product and email-notification microservices. Once we added then will be able to use the common objects across both the microservices. Post this change to validate producer and consumer microservices are able to publish and consume the events are not.
Steps to validate the Producer and Consumer.
- First bring up the kafka servers. Refer Apache Kafka Server Installation section to bringup all the kafka servers.
- Run producer microservice.
- Run Consumer microservice.
- Open the postman and hit the request to send the message
- In producer microservice the log has to be displays as Message sent successfully product-created-events-topic
- In Consumer microservice the log has to be displays as Received a new event iPhone17
Spring Bean configuration
Till now have seen how to use the configuration which are maintained in Application.properties for Kafka consumer (EmailNotificationMicroservice). The problem of using Application.properties file is, in case any value with fully qualified package name that can create a typo error, which creates a problem during execution of the service. It is not very convenient to type the entire package name, and it is very easy to make a typo.
Instead of using the Application.properties we can configure kafka consumer in Java code using spring bean. To configure Kafka consumer using Java Bean, I will need to create new configuration class as KafkaConsumerConfiguration.
package com.navabitsolutions.email.notification.ms.config;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.kafka.config.ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.ConsumerFactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonDeserializer;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class KafkaConsumerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<String, Object> consumerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> config = new HashMap<>();
config.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, environment.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers"));
config.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
config.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, JsonDeserializer.class);
config.put(JsonDeserializer.TRUSTED_PACKAGES, environment.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.properties.spring.json.trusted.packages"));
config.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, environment.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.group-id"));
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(config);
}
@Bean
public ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, Object> kafkaListenerContainerFactory(
ConsumerFactory<String, Object> consumerFactory) {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, Object> factory = new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
factory.setConsumerFactory(consumerFactory);
return factory;
}
}
Once creation of above configration class comment out the unused properties from Application.properties file. Post that we need to create the Kafka listener container factory. Add kafkaListenerContainerFactory object in above configuration class.
Updated full source code is available in GitHub repository Kafka Consumer: Email Notification Microservice