SpringBoot-Kafka Tutorial
Apache Kafka Producer: Idempotent
In the following lessons you will learn how to enable Idempotence in your Kafka producer. Idempotence is very very important concept where we can avoid storing the duplicate messages in kafka broker.
The problem without Idempotent
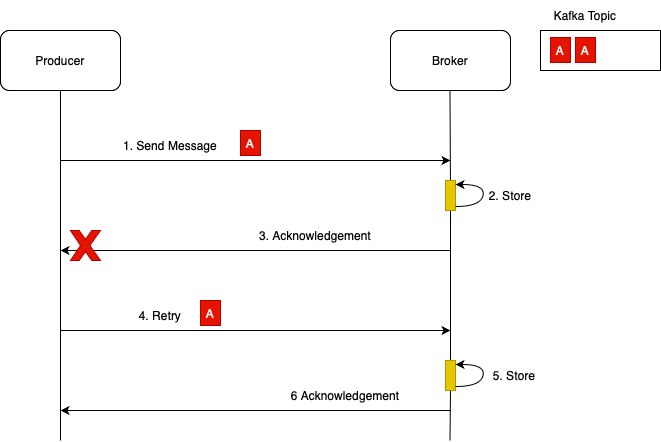
Lets condider a scenario where, left side of above diagram, I have Kafka producer and on the right side of my diagram I have Kafka Broker. Kafka producer will send a message to Kafka Broker. Broker will receive this message and it will store it in Kafka topic. Once the message is successfully stored, Kafka Broker will send back acknowledgement.
In network communication if possible that error can take place and this acknowledgement will not reach Kafka producer. If producer retries are configured, then producer will send the same message again. Broker will receive this message and it will store it in Kafka topic again. Once again the same message will be stored in kafka topic and kafka broker will send acknowledgement to kafka producer and this time the acknowledgement will pass through.
Now the problem here is that we now have two identical messages in Kafka topic. In some applications, duplicate messages might not be a very big deal, but in some applications this will be a very big problem. If it is a banking application, for example, then user's bank account can be charged twice or if it is online store, then it is possible that a product will be shipped to customer two times instead of one time.
What is Idempotent
An important is nothing but the producer to avoids duplicate messages in the log in the presence of failures and retries. In simple words, this means that producer can send the same message multiple times, but Kafka Broker will only store it once and keep it in the correct order, and this can prevent inconsistency in Kafka topic, even if there are problems with the network or servers.
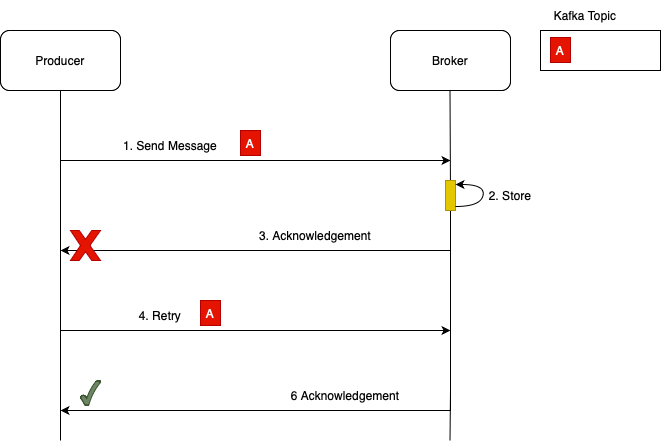
Once you enable Idempotence in your Kafka producer, your application will work like below
- 1. Producer will send a message.
- 2. Kafka broker will store this message in Kafka topic and once the message is stored, Kafka Broker will send acknowledgement back to producer.
- 3. If network problem takes place and this acknowledgement does not reach Kafka producer, then our producer will send the message again.
- 4. We have enabled Idempotence in our producer, Kafka broker will see that producer is sending the same message again. And there is already a message like this in Kafka topic. Instead of storing the same message again, Kafka Broker will simply acknowledge that it does have already this message.
- 5. If Kafka producer sends the same message multiple times, there will be only one such message in the topic and there will be no duplicates.
To enable Idempotents in your Kafka producer, you will need to set the following configuration property enable.idempotance=true
If you are using Application.properties file, then the configuration property should be like spring.kafka.producer.properties.enable.idempotance=true
If you are using bean, then your configuration property will look like this props.put(ProducerConfig.ENABLE_IDEMPOTANCE.CONFIG, true)
By default this configuration property is already set to true. So by default this configuration property is already enabled and you do not really need to enable it explicitly. However, it is still recommended to explicitly set this property to true because it is very easy to disable it
Producer Idempotence in application.properties
You need to set the following properties to enable the idempotance in kafka producer.
- 1. spring.kafka.producer.acks=all: In case if we're setting the idempotance to true then producer acks should be set to all. In case if we set the producer acks to something different value then will receive configuration exception.
- 2. spring.kafka.producer.retries=10: In case if we're not configure the retires then the producer by default it will take the maximum retries which is 2147483647
- 3. spring.kafka.producer.properties.enable.idempotance=true: By default this confgiration is set to true, its always recommended to set this value as true.
- 4. spring.kafka.producer.properties.max.in.flight.requests.per.connection=5: This should be less than or equal to 5.
Producer Idempotence using spring bean
package com.navabitsolutions.product.ms;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.admin.NewTopic;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerConfig;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.kafka.config.TopicBuilder;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.DefaultKafkaProducerFactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.ProducerFactory;
import com.navabitsolutions.product.ms.events.ProductCreatedEvent;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
@Configuration
public class KafkaConfig {
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers}")
private String bootstrapServers;
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer}")
private String keySerializer;
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer}")
private String valueSerializer;
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.acks}")
private String acks;
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.properties.delivery.timeout.ms}")
private String deliveryTimeout;
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.properties.linger.ms}")
private String linger;
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.properties.request.timeout.ms}")
private String requestTimeout;
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.properties.enable.idempotance}")
private String idempotance;
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.properties.max.in.flight.requests.per.connection}")
private String inFlightRequests;
Map>String, Object< producerConfigs() {
Map>String, Object< config = new HashMap><();
config.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, bootstrapServers);
config.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, keySerializer);
config.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, valueSerializer);
config.put(ProducerConfig.ACKS_CONFIG, acks);
config.put(ProducerConfig.DELIVERY_TIMEOUT_MS_CONFIG, deliveryTimeout);
config.put(ProducerConfig.LINGER_MS_CONFIG, linger);
config.put(ProducerConfig.REQUEST_TIMEOUT_MS_CONFIG, requestTimeout);
config.put(ProducerConfig.ENABLE_IDEMPOTENCE_CONFIG, idempotance);
config.put(ProducerConfig.MAX_IN_FLIGHT_REQUESTS_PER_CONNECTION, inFlightRequests);
return config;
}
@Bean
ProducerFactory>String, ProductCreatedEvent< producerFactory() {
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory><(producerConfigs());
}
@Bean
KafkaTemplate>String, ProductCreatedEvent< kafkaTemplate() {
return new KafkaTemplate>String, ProductCreatedEvent<(producerFactory());
}
@Bean
NewTopic createTopic() {
return TopicBuilder.name("product-created-events-topic")
.partitions(3)
.replicas(1)
.build();
}
}
Full code base is available in GitHub repository Kafka Producer: Product Microservice