SpringBoot-Kafka Tutorial
Multiple consumers in consumer group
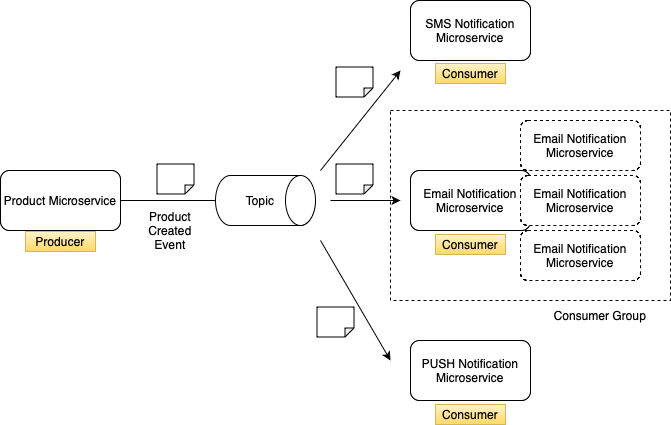
In the following lessons, you will learn how to start multiple Kafka consumers and how to make them work together as a group. Let's have a look at the above diagram on the left side, I have products microservice which acts as Kafka producer. In the middle I have Kafka topic. And on the right side in this diagram I have three different microservices that act as Kafka consumers.
When products microservice publishes product created event. This event gets stored in Kafka topic. As soon as we have new event in Kafka topic, microservices that are listening for events from this topic will consume it.
In this example I have three different microservices. So all three microservices will receive a new product created event message. And this is an example where you have multiple Kafka consumers reading from the same topic. Now this example is simple because all microservices are different, and each of them needs to receive its own copy of the product created event.
But what if we need to scale up and start more instances of email microservice?
Let's assume that we started three more email notification microservices, and now we have four of them running. In this case, when a
new message is published to a topic, SMS and Push notifications will receive its own copy but Email notification microservice has four
instances running. Do we want all four email notification microservices to consume exactly the same message? if so then 4 messages will be
send to the customer it means duplicate message will be triggered. In such cases the solution is to use the consumer group concept.
Even though we have four instances of email notification microservice running, we want only one of them to receive a new message, and it does not matter which one of these instances will process the message. We want the message to be processed one time only. So to help us scale up consumer microservice, Kafka allows us to run multiple consumers in a group, and this is called consumer group. Running multiple consumer microservices in a group is very helpful when you have lots of messages in the topic, and you need to process them faster. In this case, you can start up multiple instances of email notification microservice, group them into one consumer group, and have each group member pick one message from the topic. And in this case, messages that are stored in the topic will be processed much faster because instead of one microservice, you now have multiple copies of this microservice working. But even though you have multiple instances of the same microservice working, when a new message gets into the topic, it will be processed one time only by one of these instances in the consumer group.
Rebalancing Consumers and Partition assignment
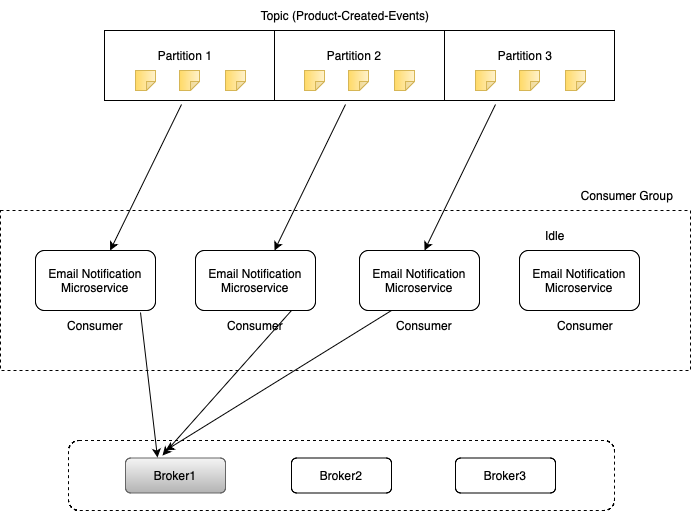
Let's learn a little bit more about consumers, consumer groups and how they read data from Kafka Topic and its partitions. It is important to understand how this works, because it will help you decide how many partitions to create in a topic and how many microservices you can start if you want to scale up your application.
So let's assume that we have Kafka topic that is called product created events. We created this topic with three partitions. All messages in this Kafka topic will be stored in this three separate partitions. And to consume messages from this topic we started one microservice that is called email notification microservice. And this microservice acts as Kafka consumer.
When we have only one consumer microservice, then this consumer will read messages from all three partitions in a topic. Now let's assume that there is a large load on our application, and one instance of email notification microservice is not enough. We want to scale up our application, and we want to start up one more instance of email notification microservice.
What will happen now is Kafka will notice that we have two consumer applications running and it will reassign partitions among these two consumer applications. Now it is not one consumer application that reads from all three partitions. Now one instance of email notification microservice reads messages from one partition and another instance of email notification microservice reads data from two partitions. This process of automatic partition reassignment is called rebalancing.
It happens very quickly, but while partitions are being reassigned, consumers stop consuming messages from topic for a moment. And rebalancing takes place every time a new consumer joins a consumer group, and every time existing consumer leaves consumer group. For example, if we decide to scale up our application even more, and if we decide to start up one more email notification microservice, then partition rebalancing will automatically take place again and partitions will be reassigned again. And during this partition reassignment, Kafka is trying to make sure that each partition is consumed by one consumer in a group.
Once rebalancing is complete, all consumers in the group will continue to consume messages from their assigned partitions in parallel. Now, let's assume that we want to scale up our application even further, and we want to start up one more instance of email notification microservice. Unfortunately, this instance will sit idle in Kafka. Two consumers from the same consumer group cannot read messages from the same partition. And this is a very important moment to understand. You cannot start more consumers than the number of partitions you have in the topic.
If your topic has only one partition, then you can start only one consumer microservice. If your topic has three partitions, then you can scale your application by starting three instances only.
Now when you start a new Kafka consumer application and it joins consumer group, this new Kafka consumer application starts sending signals to one of the brokers that is selected as a group coordinator. These signals, they are called heartbeats and they are sent at irregular time intervals. This time interval can be configured, but the default value is 3 seconds.
So while your Kafka consumer microservices are running, each of them will be sending heartbeat signals to Kafka Broker, letting it know that I'm running and I can consume new messages. If one of these Kafka consumers stops, then it also stops sending heartbeat signals to Kafka Broker. When Kafka Broker notices that there are no heartbeats coming from consumer, it will remove this consumer from consumer group and it will initiate rebalancing.
It will check how many consumers are running and how many partitions you have in Kafka topic, and it will reassign partitions, trying to make sure that each partition is read by one consumer. Remember that two consumers cannot read from the same partition, and when rebalancing completes, all consumers in the group will resume consuming messages from newly assigned partitions in parallel.
Assigning Microservice to a consumer group
in Apache Kafka the consumer group can be assigned in three different ways
- 1. Using KafkaListener annotation like following @KafkaListener(topics="product-created-events-topic", groupId="product-created-events")
- 2. Another way is with the help of consumer factory configurations like following config.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, environment.getProperty("consumer.group-id"));
- 3. Another way is with the help of application properties like following spring.kafka.consumer.group-id=product-created-events
Starting up more microservices
To start multiple instances of your microservice first we need to validate the port configuration. In application.properties file the
server.port must be configured as 0. It means when ever we try to start our application the system will assign the random port number and
bring up the server.
server.port=0
The best way to start the multiple instances are with the help of terminal, open the terminal or command prompt and navigate to the home directory
of your project and run the below command. Example if you want to bring up 3 instances then we need to open three new differenct tabs in terminal
or command prompt and then we need to run the below command.
mvn spring-boot:run
Multiple Consumers consuming messages from Kafka topic
If we have multiple consumers which belongs to same consumer group and these consumers are trying to consumer messages from the same topic then only one consumer will receive the message. Other consumers will not receive the same message. This can be achived using the consumer group concept.